BACK
What is an API?
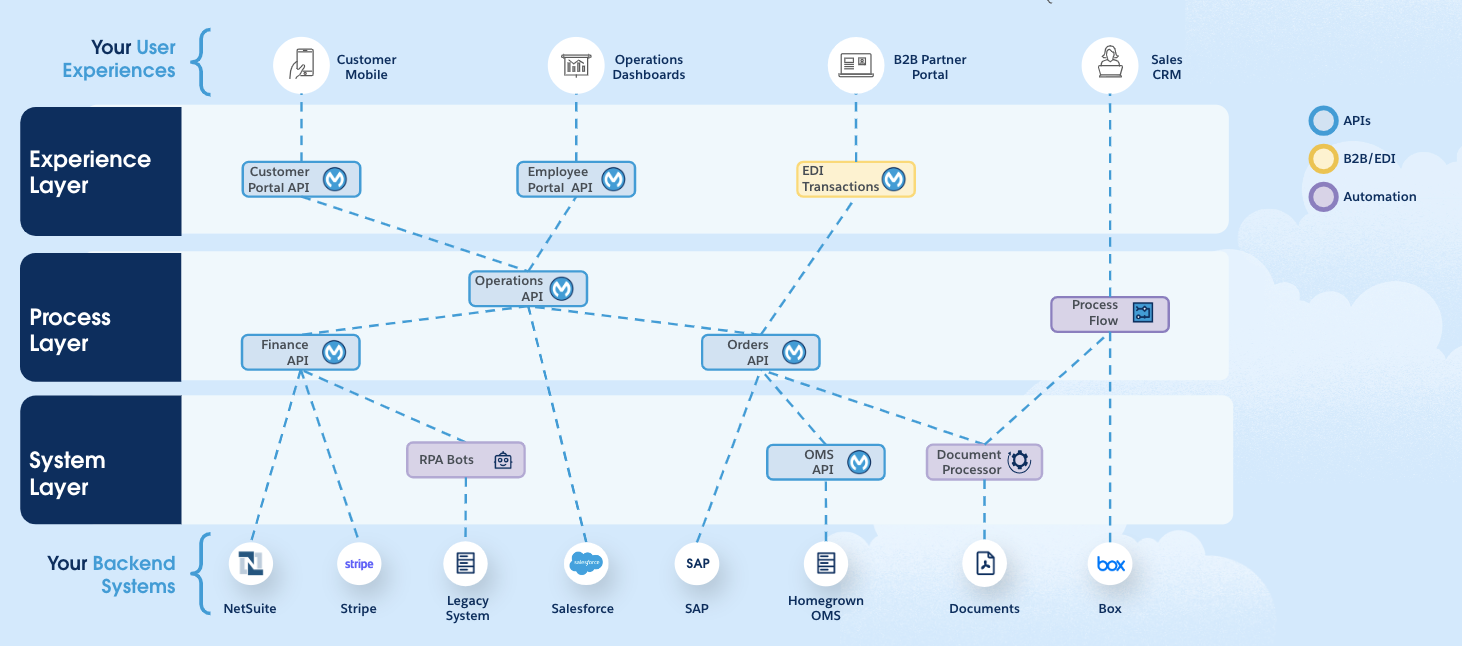
How APIs Work
Core Operation
Request / Response Cycle
Why is the API Layer Important?
Endpoints and Methods
What is an Endpoint?
Role of HTTP Methods
Use of Path, Query, and Body
Status Codes and Error Handling
API Types
Public / Open API
Partner API
Internal / Private API
Composite API
Protocol and Style-Based Types
API Design & Best Practices
Resource-Oriented Design
Versioning
Contract-Based Development
Developer Experience
Authentication & Security
Basic Security Measures
Role of API Gateway
Security Testing and Processes
Management & Control
API Catalog and Lifecycle Management
Policy & Compliance
Performance & Observability
Benefits of APIs
Faster Innovation & Time-to-Market
Cost Efficiency & Reduced Technical Debt
New Business Models & Ecosystems
Improved Customer Experience
Common Use Cases
System Integrations (CRM, ERP, Supply Chain)
Backend Services for Mobile & Web Apps
Partner Portals & B2B Integration
IoT and Real-Time Data Streams
Microservice Architectures
Implementation Roadmap
1. Preparation & Discovery
2. Pilot & Prototype
3. Scaling & Platform Setup
4. Operations & Continuous Improvement
5. Value Measurement
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an API?
What do endpoint and method mean?
What is the main difference between REST and GraphQL?
What security measures should be taken for APIs?
What is API-led Connectivity and why is it important?
How should I get started?
Start Your API Strategy with Logicalbond
API Consulting & Value Analysis
Pilot Projects & Accelerators
Platform & Operational Support
Training & Developer Ecosystem
Compliance & Local Requirements
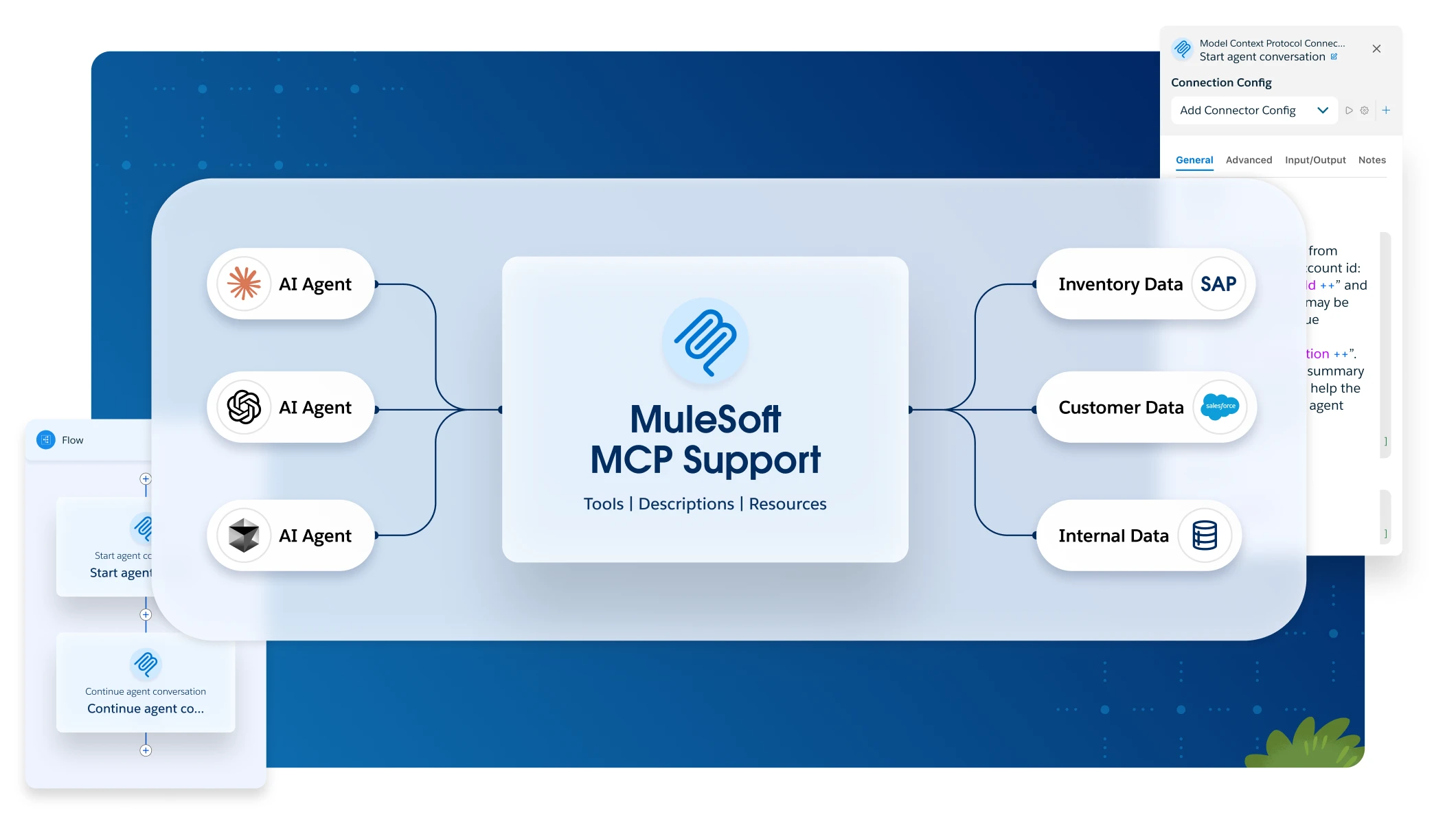
What is MCP?
MCP (Model Context Protocol) is a protocol that standardizes agent-to-tool and agent-to-system communication. MuleSoft's Anypoint Platform MCP support allows organizations to convert existing Mule applications and APIs into agent-ready assets with minimal changes, enabling agents to discover and invoke them. This ensures more accurate results with real-time business context, reduces hallucination risks, and scales operational automation.
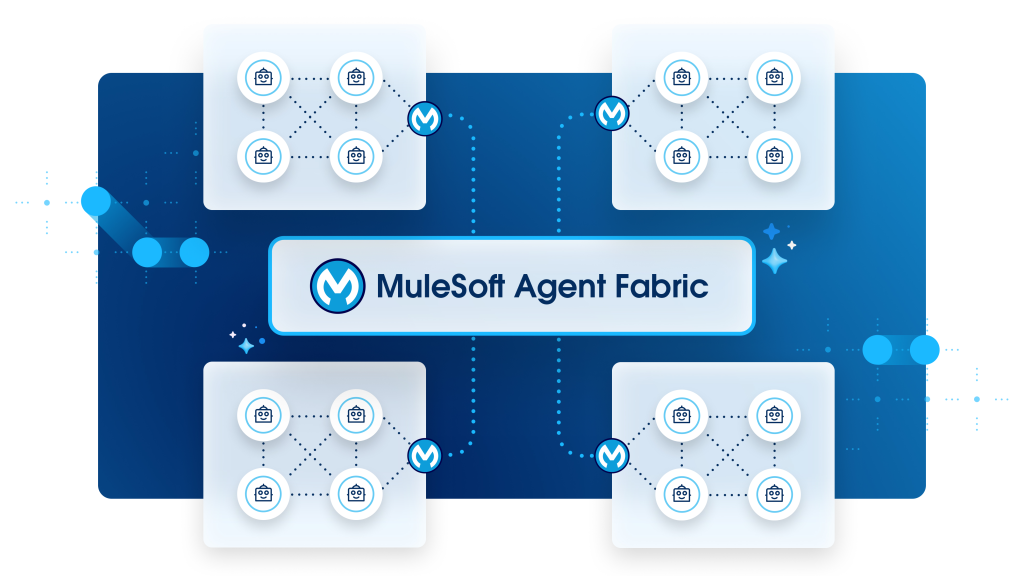
MuleSoft Agent Fabric
Agent Fabric unifies distributed and heterogeneous agent ecosystems under a single management plane. Through Agent Registry for discovery, Agent Broker for context-aware orchestration, Flex Gateway for MCP/A2A policy enforcement, and Agent Visualizer for observability, enterprises gain a secure, scalable, and transparent approach to agent management.
Anypoint Platform
Businesses require a fast, secure, and flexible integration layer across SaaS apps, on-premise systems, databases, and cloud services. MuleSoft Anypoint Platform offers an API-driven approach to manage all your enterprise systems from a single point. LogicalBond, as MuleSoft's authorized partner in Turkey, supports end-to-end digital transformation journeys for organizations.

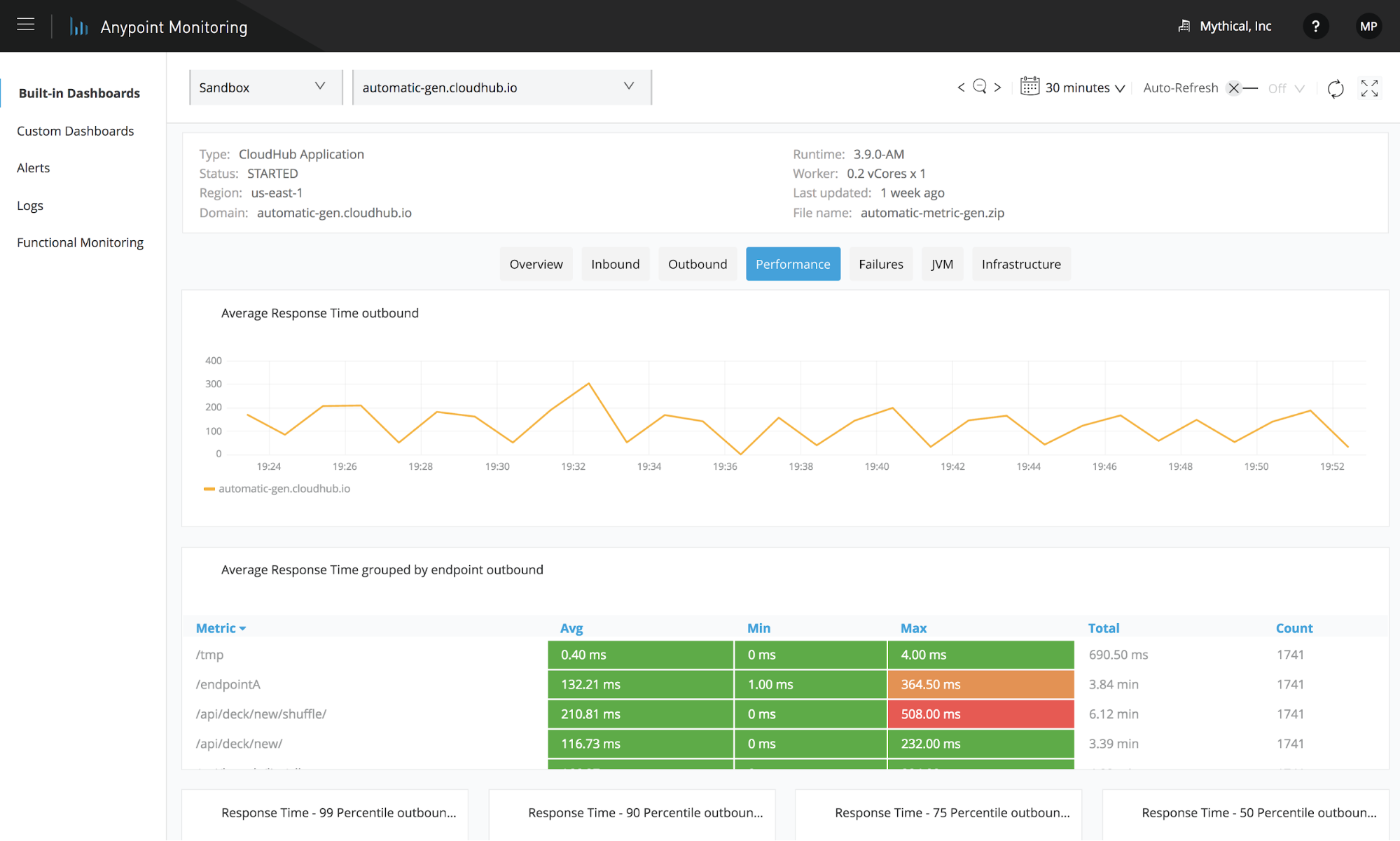
Anypoint Monitoring
Today, integration networks, APIs, and microservice architectures are critical components of enterprise digital transformation. End-to-end visibility is essential to ensure the performance, reliability, and currency of these systems. Anypoint Monitoring delivers real-time monitoring, logging, and telemetry across your entire API and integration ecosystem. As a MuleSoft partner in Turkey, Logicalbond configures this solution specifically for your organization.
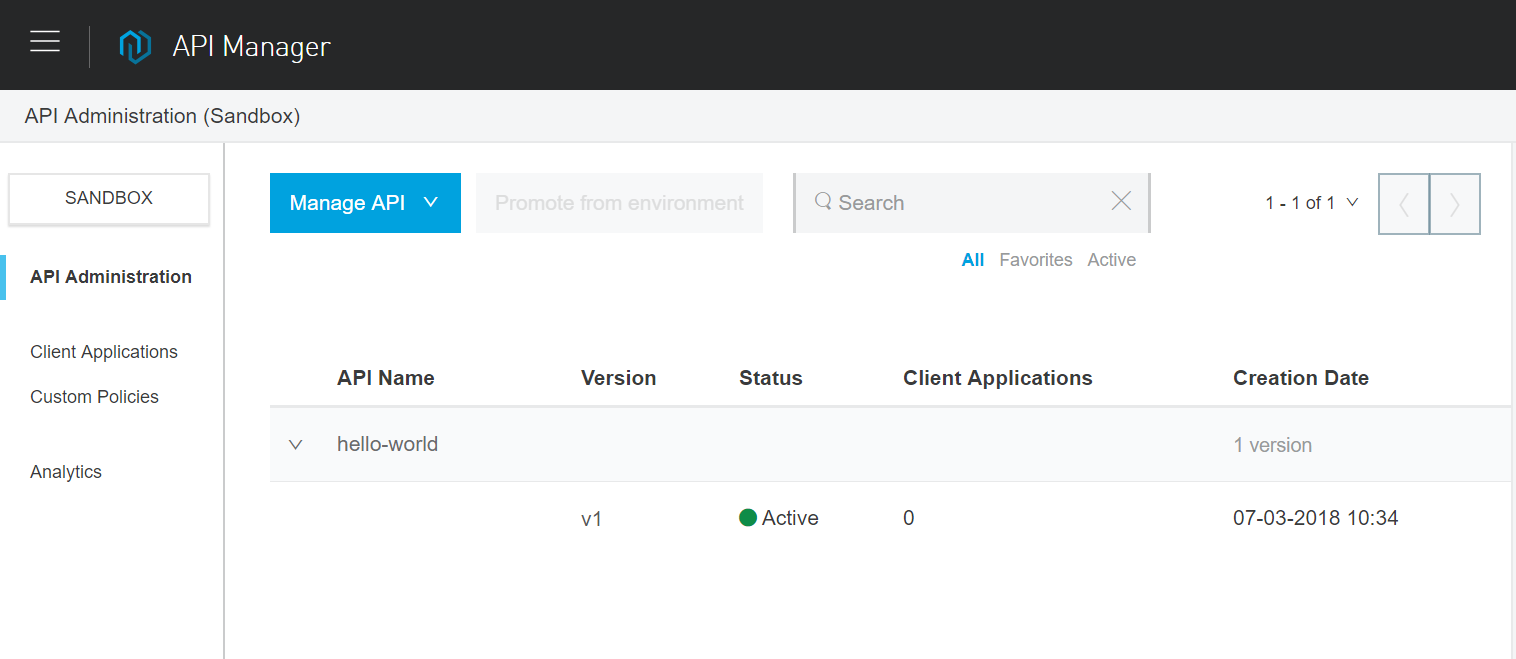
API Management
Today, organizations not only develop APIs for internal and external stakeholders but also need to manage their security, governance, performance, and consumer access. Anypoint API Manager provides an end-to-end solution for API lifecycle management. In Turkey, as an authorized MuleSoft partner, Logicalbond implements this solution tailored to your organization.
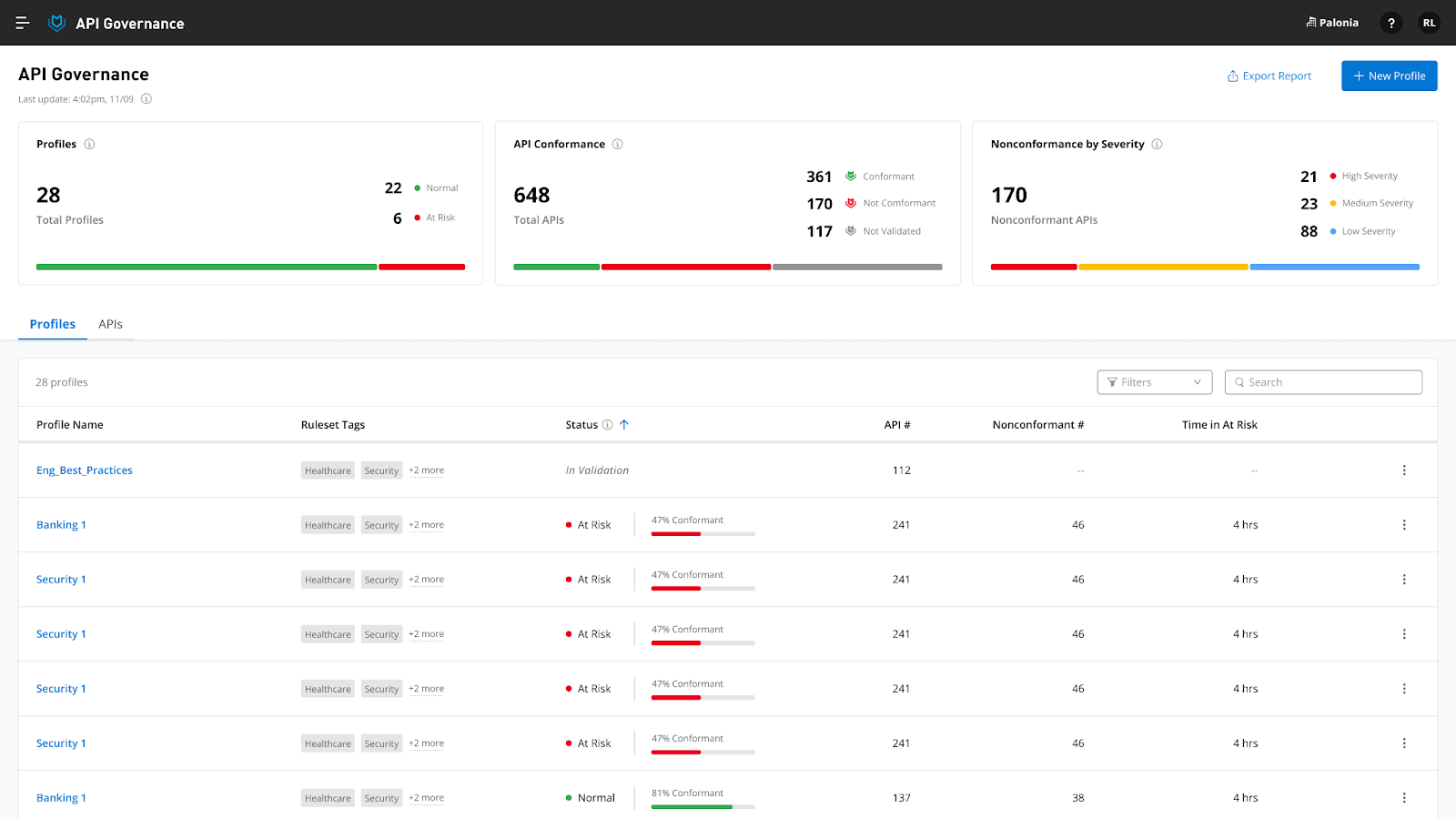
API Governance
Enterprise API management is not just about connectivity or data movement; it also ensures APIs meet quality, security, and reusability standards. Anypoint API Governance provides a robust solution for applying standards throughout the entire API lifecycle (design, development, deployment, consumption). Logicalbond, as an official MuleSoft partner, positions this solution for organizations in a tailored way.
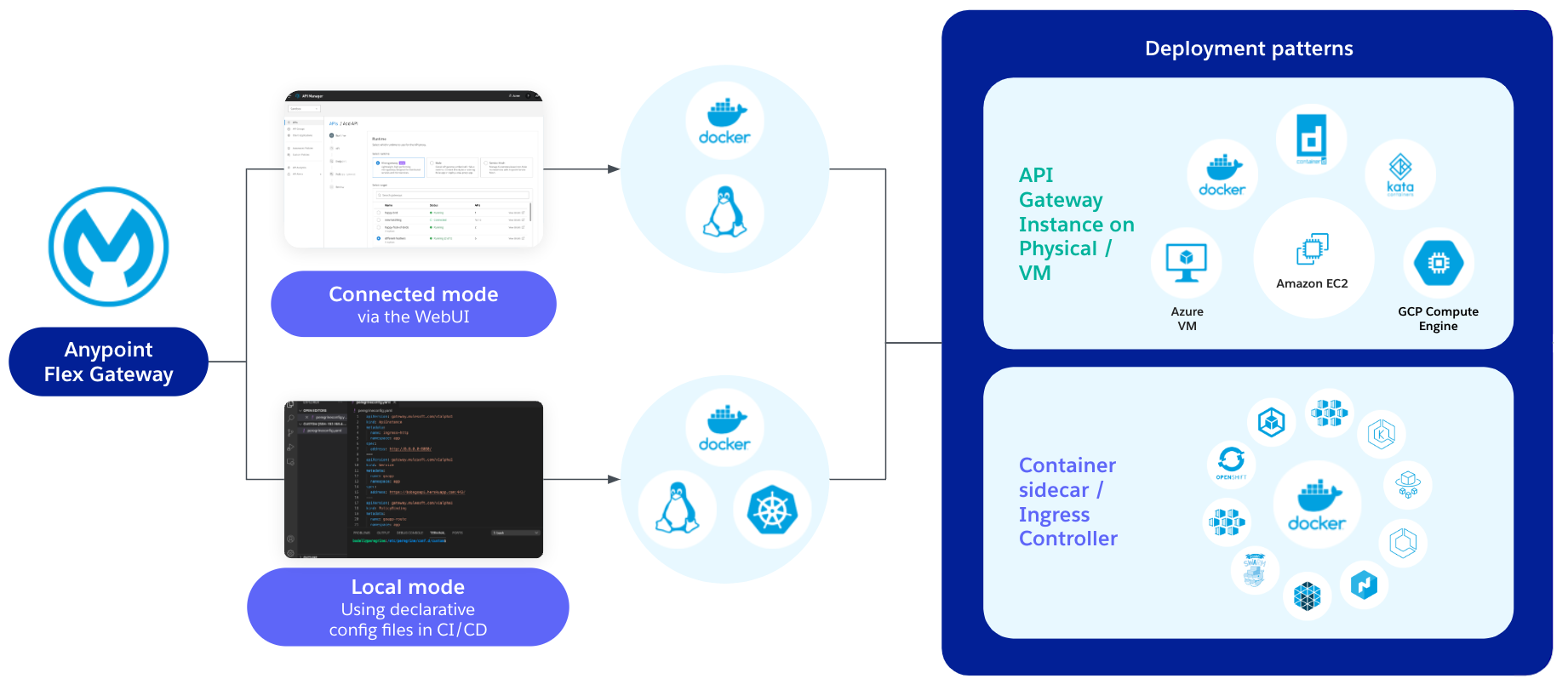
Flex Gateway
Modern enterprises do more than just develop and publish APIs; they require managing services across cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments, as well as across various technologies such as REST, SOAP, and microservices, through a single gateway layer. Anypoint Flex Gateway is designed to meet this need with high performance and robust security. Logicalbond, as an authorized MuleSoft partner, configures and implements this solution tailored to your organization.